COmoving Computer Acceleration (COCA): N-body simulations in an emulated frame of reference
Published in A&A, 2025
Recommended citation: D.J. Bartlett, M. Chiarenza, L. Doeser and F. Leclercq (2025). "COmoving Computer Acceleration (COCA): N-body simulations in an emulated frame of reference." A&A, 694, A287.
Abstract
N-body simulations are computationally expensive, so machine-learning (ML)-based emulation techniques have emerged as a way to increase their speed. Although fast, surrogate models have limited trustworthiness due to potentially substantial emulation errors that current approaches cannot correct for. To alleviate this problem, we introduce COmoving Computer Acceleration (COCA), a hybrid framework interfacing ML with an N-body simulator. The correct physical equations of motion are solved in an emulated frame of reference, so that any emulation error is corrected by design. This approach corresponds to solving for the perturbation of particle trajectories around the machine-learnt solution, which is computationally cheaper than obtaining the full solution, yet is guaranteed to converge to the truth as one increases the number of force evaluations. Although applicable to any ML algorithm and N-body simulator, this approach is assessed in the particular case of particle-mesh cosmological simulations in a frame of reference predicted by a convolutional neural network, where the time dependence is encoded as an additional input parameter to the network. COCA efficiently reduces emulation errors in particle trajectories, requiring far fewer force evaluations than running the corresponding simulation without ML. We obtain accurate final density and velocity fields for a reduced computational budget. We demonstrate that this method shows robustness when applied to examples outside the range of the training data. When compared to the direct emulation of the Lagrangian displacement field using the same training resources, COCA’s ability to correct emulation errors results in more accurate predictions. COCA makes N-body simulations cheaper by skipping unnecessary force evaluations, while still solving the correct equations of motion and correcting for emulation errors made by ML.
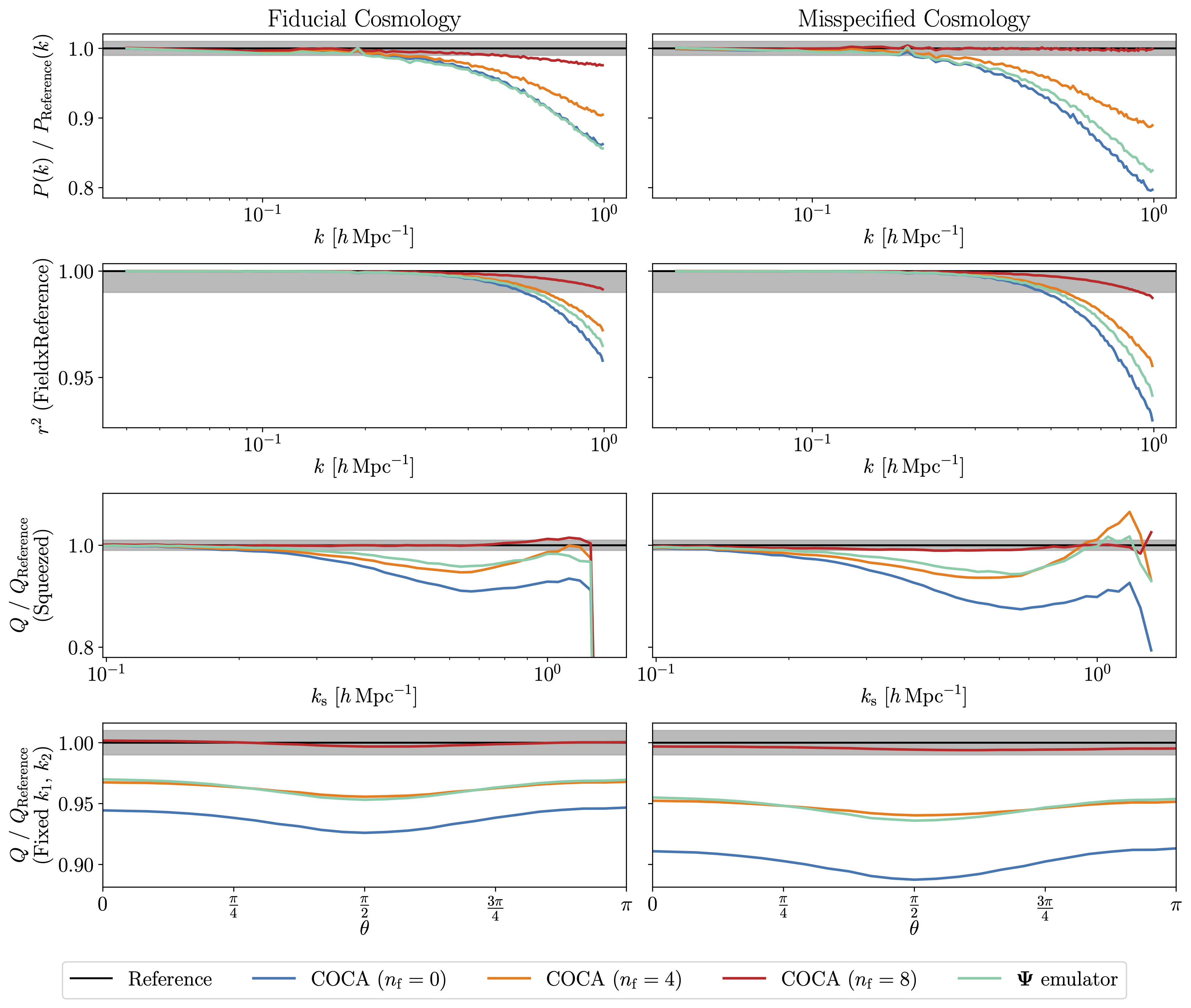 Relative performance of COCA versus an emulator of the displacement field $\Psi$. We compute the summary statistics outlined in Section III E for the final ($a=1$) matter density field and compare results at both the training cosmology and a misspecified one. Although directly emulating $\Psi$ produces a more accurate density field than simply emulating the momentum field $\textbf{p}$ (with $n_{\rm f} = 0$), using the COCA framework (emulating the frame of reference and employing additional force evaluations) yields the best performance.
Relative performance of COCA versus an emulator of the displacement field $\Psi$. We compute the summary statistics outlined in Section III E for the final ($a=1$) matter density field and compare results at both the training cosmology and a misspecified one. Although directly emulating $\Psi$ produces a more accurate density field than simply emulating the momentum field $\textbf{p}$ (with $n_{\rm f} = 0$), using the COCA framework (emulating the frame of reference and employing additional force evaluations) yields the best performance.
